Automatic parameter selection¶
This example contains the simulation of a plane wave (oblique incidence), scattered by a spiral of nine aluminum disks on a thin-film waveguide structure supported by a glass substrate
Click here
to download the Python script.
Test balloon simulation¶
The first part of the script runs a test balloon simulation, where the ensemble of nine disks is replaced by a single disk. An automatic parameter selection is triggered for the test balloon simulation. See the section on Automatic parameter selection for a description of the feature.
Actual simulation¶
In the second part of the script, the resulting parameters (l_max, m_max, neff_max, neff_resolution) are copied to the actual simulation settings and the actual nine-particle simulation is run.
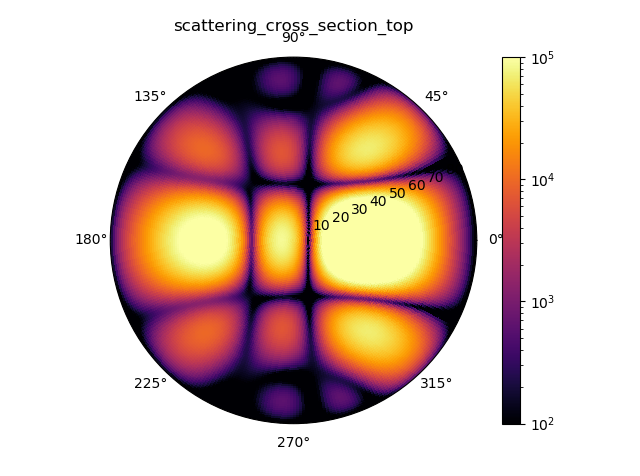
ambient DSCS |
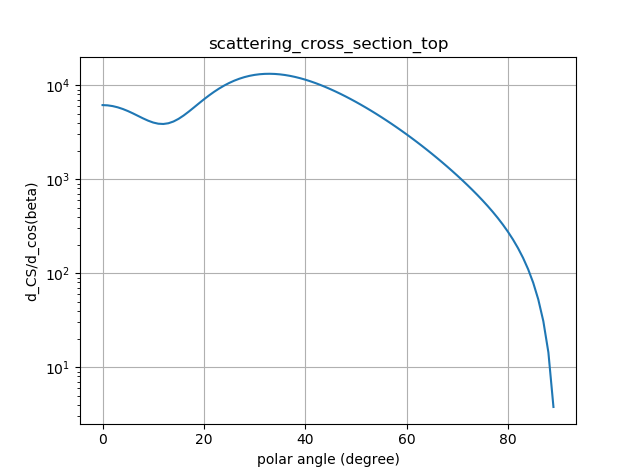
ambient DSCS (integrated over \(\alpha\)) |
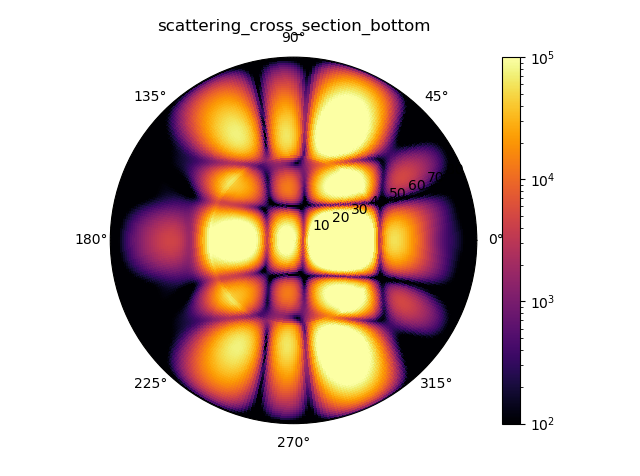
substrate DSCS |
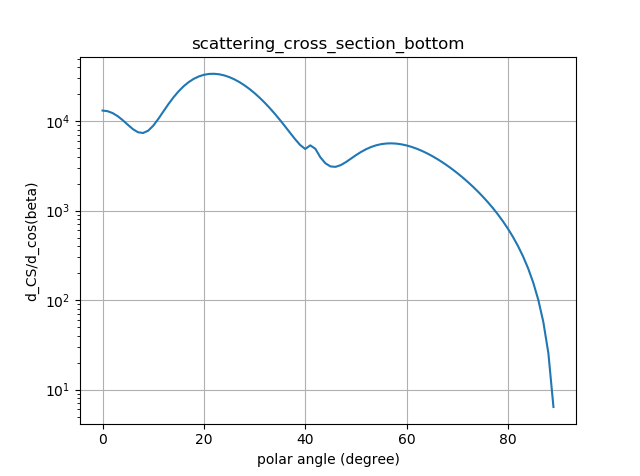
substrate DSCS (integrated over \(\alpha\)) |
After the simulation has run, the differential scattering cross section is evaluated in a post processing step. The left column shows the 2D-differential scattering cross section, \(\mathrm{DSCS}(\alpha, \beta) = \frac{\mathrm{dSCS}}{\mathrm{d}\Omega}\), whereas the right column shows the 1D distribution (i.e., the integral over the azimuthal direction coordinate), \(\mathrm{DSCS}(\beta) = \frac{\mathrm{dSCS}}{\mathrm{d}\cos\beta}\).
In the substrate far field, the critical angle is visible as a ring-shaped feature.